Seamless/Continuity Editing
This is also known as classical or invisible editing. Its
basically straight forward cuts that flow in a clear and logical way. The
editing is so good that it is unnoticeable.
Here is my TV Advertisement that I made with my group, as an
example:
Motivated Editing
These are cuts motivated by a purpose. The purpose could be
a narrative, character or emotion. When the first shot cuts to the second shot,
shot one provides a motive for shot two. This way of editing is often used in
horror films and documentaries.
Montage Editing
Editing which includes a lot of fast paced shots, which are
strung together in a fast paced sequence in a way that compress time and gives
a lot of information in a short amount of time.
For example, the Montage Song in Team America.
This clip shows the character training and getting ready for something which would have taken much longer had it not been in a montage. It helps to reduce the time needed while still giving the same amount of information.
The Jump Cut
This is the transition between two cuts, which appear to
jump. These cuts help to pass time.
Examples of jump cuts:
These cuts are used often in interviews in documentaries - jumping from one person to the next showing who is speaking.
Parallel Editing
Also known as cross cutting. This technique includes
alternating two or more scenes showing things happening at the same time but in
different locations. It is used to add interest and excitement as well as
suspense.
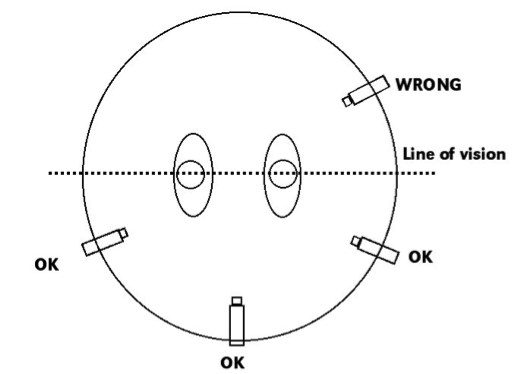
The 180 Degree Rule
This rule refers to an imaginary line, which cuts through
the middle of the scene from one side to another. The line is not to be crossed
as crossing it would change the viewer’s perspective in a way, which would
cause disorientation and confusion.
|
|
Diagram of 180
degree rule
|
Cut Aways
A quick shot of something other than the action. Can be a
different subject, for example a cat when the main subject is the owner, or a
close up of a different part of the actual subject like the hand or mouth. This
is used as a buffer between shots and helps to add interest or information.
They also help to cover up jump cuts in things like interviews.
Example:
The cutaways used here are to keep the video visually stimulating since theres something different to look at while listening to someone drone on and on. And the cut aways also hide jump shots and make the overall video flow better.
No comments:
Post a Comment